As we delve into the fascinating realm of stable isotopes, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of scientific precision and exploration. Predict the stable isotope in each pair takes center stage, setting the tone for an engaging journey through the principles, applications, and significance of stable isotope analysis.
Stable isotopes, ubiquitous in nature, offer invaluable insights into diverse scientific disciplines. Their unique properties and predictable behaviors have propelled them to the forefront of environmental science, archaeology, forensics, and beyond. This introductory paragraph provides a captivating overview of the topic, laying the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of stable isotope analysis.
Stable Isotope Basics
Stable isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. They occur naturally in the environment and have the same chemical properties but different masses. Stable isotopes are significant because their ratios can provide insights into various environmental, biological, and geological processes.
Common examples of stable isotopes include carbon-12 and carbon-13, nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15, and oxygen-16 and oxygen-18.
Methods for Predicting Stable Isotopes: Predict The Stable Isotope In Each Pair
Various analytical techniques are used to predict stable isotopes, including:
- Mass spectrometry:This technique separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, allowing for the identification and quantification of different isotopes.
- Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS):This technique combines gas chromatography with mass spectrometry to separate and identify volatile organic compounds, including stable isotopes.
- Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS):This technique uses a laser to vaporize a sample and then analyzes the emitted light to determine the elemental and isotopic composition.
Factors Influencing Stable Isotope Ratios
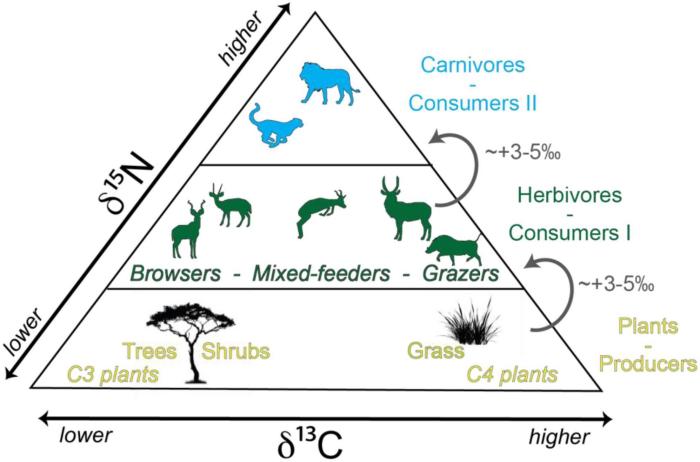
Stable isotope ratios can be influenced by several environmental and biological factors, including:
- Temperature:Isotope fractionation can occur during chemical reactions and physical processes that are temperature-dependent.
- pH:Isotope fractionation can also occur in acidic or basic environments, affecting the relative abundances of different isotopes.
- Biological processes:Certain biological processes, such as photosynthesis and respiration, can fractionate isotopes, leading to variations in their ratios.
- Geographic location:Isotope ratios can vary geographically due to differences in climate, geology, and other environmental factors.
Applications of Stable Isotope Analysis
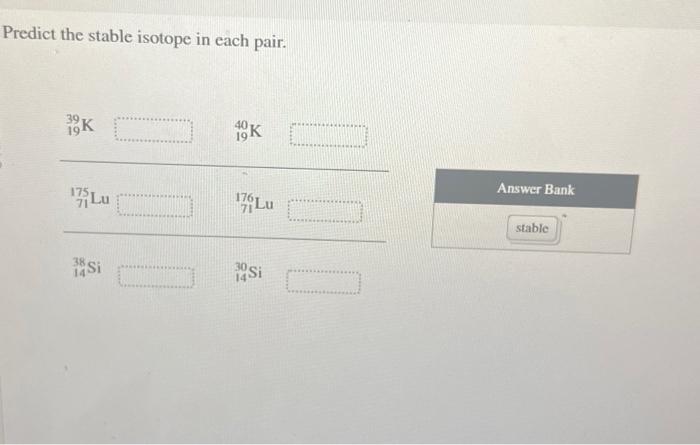
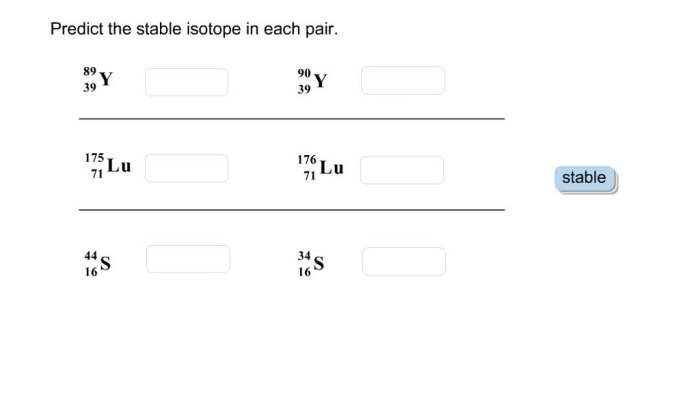
Stable isotope analysis has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Environmental science:Stable isotopes are used to study ecosystem dynamics, food webs, and the cycling of nutrients in the environment.
- Archaeology:Stable isotope analysis helps determine the diet, migration patterns, and environmental conditions of past populations.
- Forensics:Stable isotopes can be used to identify the origin of materials, such as food, drugs, and human remains.
- Medicine:Stable isotopes are used in medical diagnostics, such as breath tests for detecting metabolic disorders.
Comparison of Stable Isotopes in Pairs
| Element | Stable Isotopes | Atomic Mass | Relative Abundance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1H, 2H | 1.0078, 2.0141 | 99.985%, 0.015% | Nuclear reactions, isotopic labeling |
| Carbon | 12C, 13C | 12.0000, 13.0034 | 98.89%, 1.11% | Radiocarbon dating, environmental studies |
| Nitrogen | 14N, 15N | 14.0031, 15.0001 | 99.634%, 0.366% | Fertilizer studies, atmospheric chemistry |
| Oxygen | 16O, 18O | 15.9949, 17.9992 | 99.76%, 0.205% | Paleoclimatology, water tracing |
Top FAQs
What are stable isotopes?
Stable isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. They do not undergo radioactive decay, making them ideal for various scientific applications.
How are stable isotopes used in environmental science?
Stable isotope analysis is widely used in environmental science to trace the movement of water, nutrients, and pollutants through ecosystems. It provides valuable insights into biogeochemical cycles and helps identify sources of contamination.
What role do stable isotopes play in archaeology?
Stable isotope analysis of archaeological materials, such as bones, teeth, and artifacts, provides information about ancient diets, migration patterns, and environmental conditions. It helps reconstruct past climates and ecosystems, shedding light on human history and evolution.