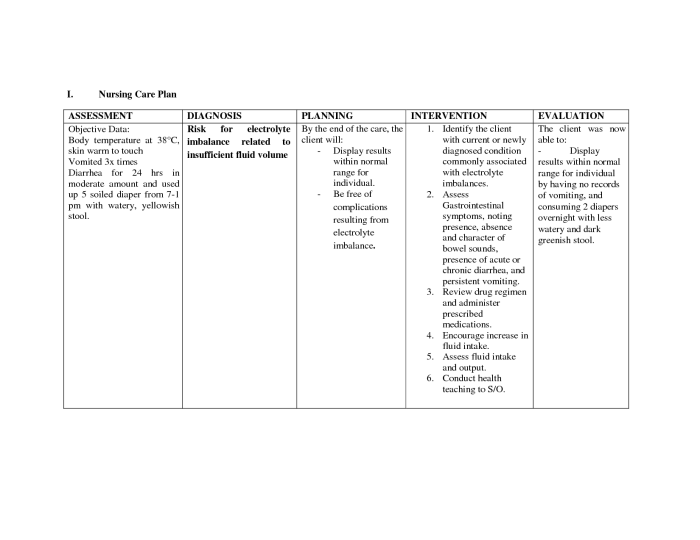
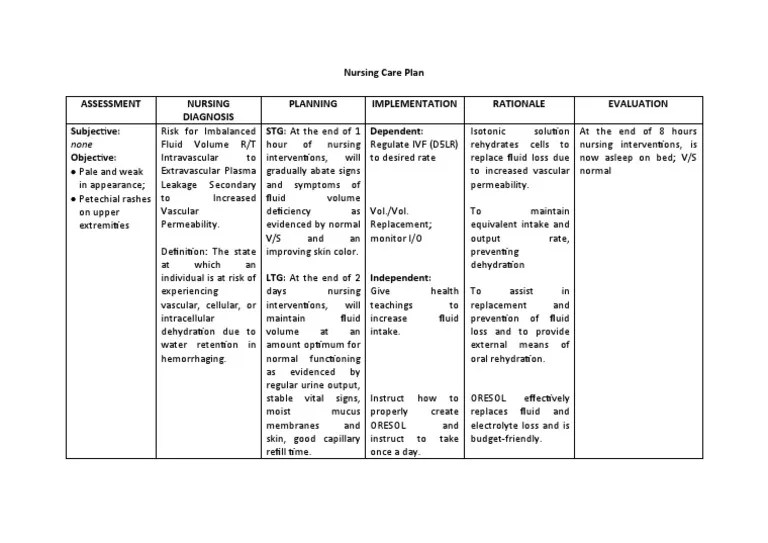
Risk for electrolyte imbalance ncp takes center stage as a critical concern in healthcare, demanding a comprehensive understanding among healthcare professionals. This guide delves into the physiological mechanisms, clinical manifestations, assessment, nursing care, prevention, and management of electrolyte imbalances, providing an authoritative resource for evidence-based practice.
Electrolyte imbalances can arise from various factors, including medical conditions, medications, age, diet, and lifestyle choices. Recognizing the signs and symptoms associated with different types of electrolyte imbalances is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate interventions.
Risk Factors for Electrolyte Imbalance: Risk For Electrolyte Imbalance Ncp
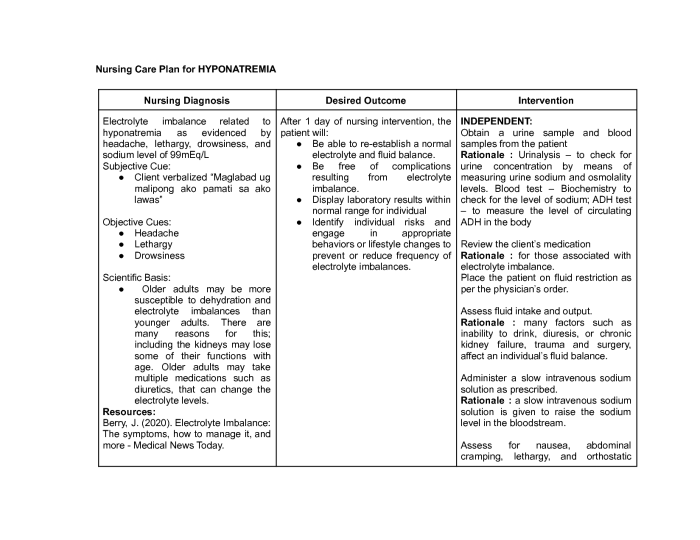
Electrolyte imbalances can occur due to a variety of factors, including physiological mechanisms, medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle choices.
Physiological Mechanisms
- Impaired renal function: The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating electrolyte balance by filtering and reabsorbing electrolytes from the blood.
- Excessive sweating: Sweating can lead to the loss of electrolytes, especially sodium and potassium.
- Gastrointestinal losses: Vomiting, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues can cause significant electrolyte depletion.
Medical Conditions
- Diabetes mellitus: Diabetes can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyperglycemia and hypokalemia.
- Addison’s disease: This condition affects the adrenal glands, resulting in decreased production of hormones that regulate electrolyte balance.
- Cushing’s syndrome: This condition causes an excess of cortisol, which can lead to electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia.
Medications
- Diuretics: These medications increase urine output, which can lead to electrolyte depletion.
- ACE inhibitors: These medications can cause hyperkalemia.
- Lithium: This medication can cause hypothyroidism and hypocalcemia.
Age, Diet, and Lifestyle Factors, Risk for electrolyte imbalance ncp
- Age: Older adults are more prone to electrolyte imbalances due to decreased kidney function and reduced electrolyte intake.
- Diet: A diet low in electrolytes can increase the risk of electrolyte imbalances.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Alcohol can interfere with electrolyte balance by promoting dehydration and diuresis.
Popular Questions
What are the common causes of electrolyte imbalances?
Electrolyte imbalances can result from various causes, including dehydration, excessive fluid loss, kidney disease, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions.
How are electrolyte imbalances diagnosed?
Electrolyte imbalances are typically diagnosed through laboratory tests that measure electrolyte levels in the blood or urine. These tests can provide valuable insights into the type and severity of the imbalance.
What are the potential complications of electrolyte imbalances?
Untreated electrolyte imbalances can lead to serious complications, including muscle weakness, cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, and even death. Prompt diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent these adverse outcomes.